<目次>
(1) C++のfork関数の構文や使い方について
(1-1) fork()関数とは?概要や目的
(1-2) fork()関数の構文
(1-3) fork()関数のサンプルプログラム(疎通レベル)
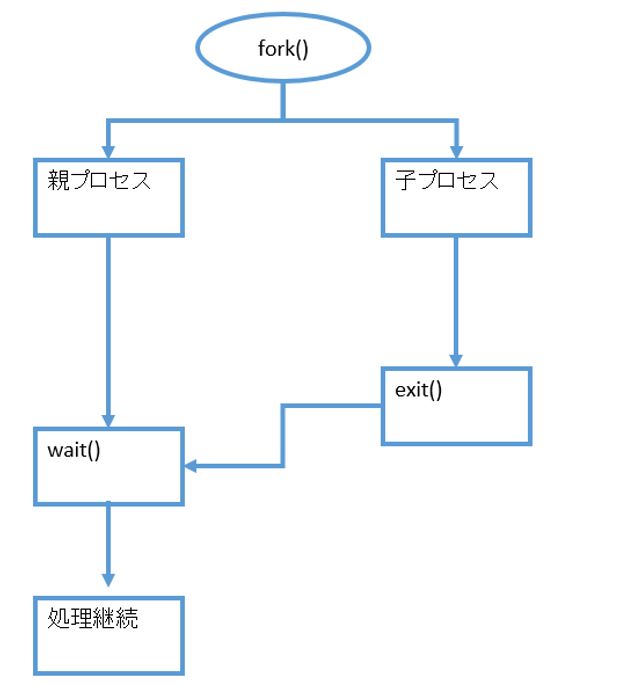
(1-4) forkでの親と子の待ち合わせ
(1-5) (参考)fork()とforループを組み合わせて複数の子プロセスを起動する
(1) C++のfork関数の構文や使い方について
(1-1) fork()関数とは?概要や目的
(1-2) fork()関数の構文
(構文)
pid_t fork()
(1-3) fork()関数のサンプルプログラム(疎通レベル)
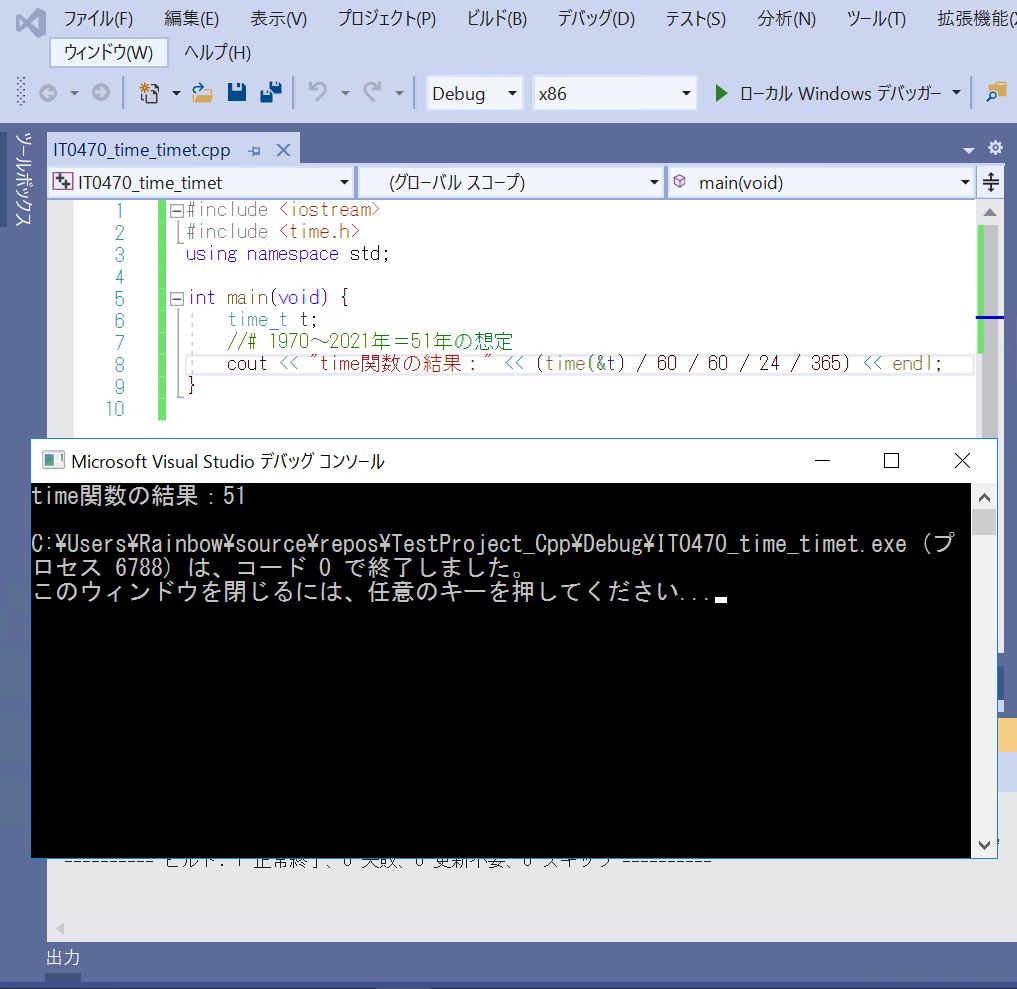
(サンプルプログラム)
#include <iostream>
//#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// fork()で子プロセスを生成(親と全く同じ動作)
fork();
cout << "Hello world Rainbow !\n" << endl;
return 0;
}
(図131)
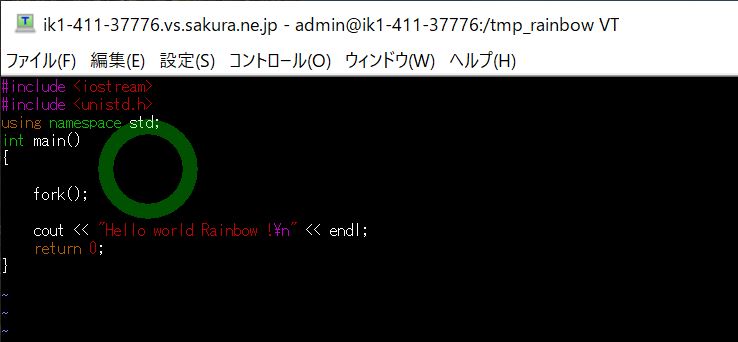

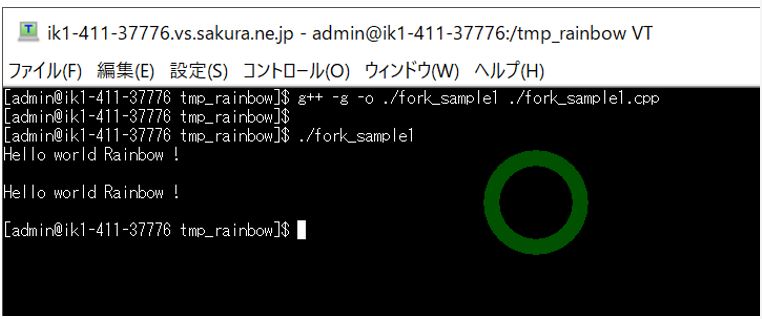
●実行結果
(1-4) fork()forkでの親と子の待ち合わせ
●forkでの親と子の待ち合わせのサンプルプログラム
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
//# 子プロセスを起動
pid_t pid = fork();
//# pid==0、つまり子プロセスの場合
if(pid == 0) {
//# 子プロセスの親プロセスPIDと、自身のPIDを出力
cout << "###[Child Process] (1)PPID: "<< getppid() <<" (2)PID: "<< getpid() << endl;
//# 子プロセスの処理終了
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else if(pid > 0) {
//# 親プロセスのPIDを出力
cout << "###[Parent Process] (1)PID: "<< getpid() << endl;
cout << "###[Parent Process] Wait for Child Process to finish. " << endl;
//# 子プロセスの処理終了を待つ
wait(NULL);
cout << "###[Parent Process] Child process finished. " << endl;
}
else {
cout << "###[Parent Process] Failed to create child process. " << endl;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
(図151)①
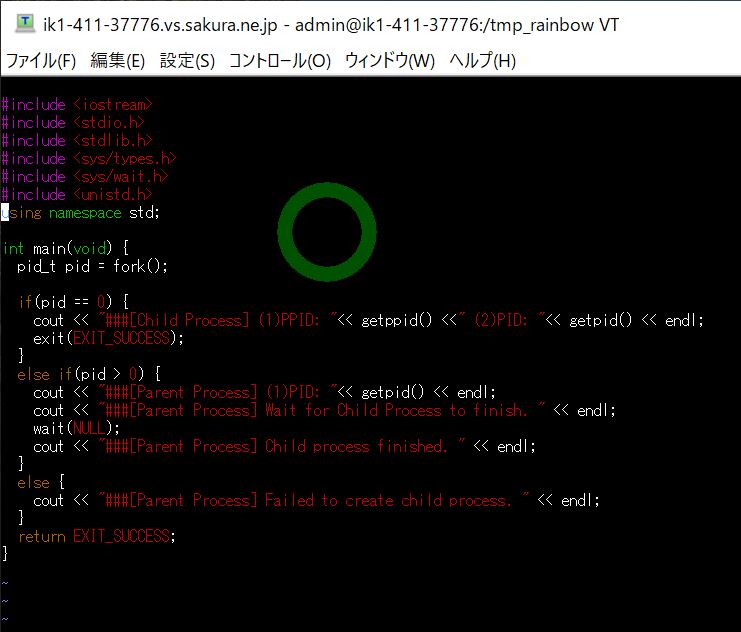
●実行結果
子プロセスを生成後、親プロセスでは「子プロセスの終了待ち(wait)」を行います。
(図151)②
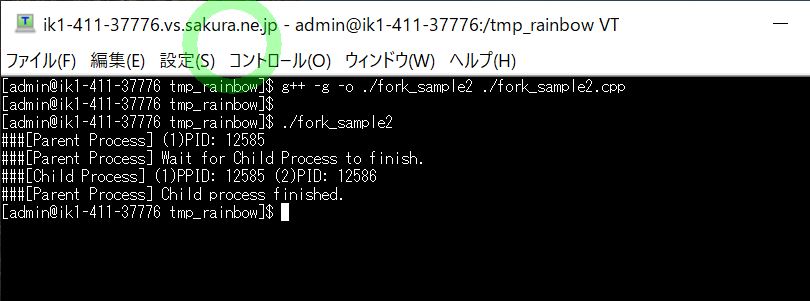
(結果例)
[admin@ik1-411-37776 tmp_rainbow]$ g++ -g -o ./fork_sample2 ./fork_sample2.cpp [admin@ik1-411-37776 tmp_rainbow]$ [admin@ik1-411-37776 tmp_rainbow]$ ./fork_sample2 ###[Parent Process] (1)PID: 12585 ###[Parent Process] Wait for Child Process to finish. ###[Child Process] (1)PPID: 12585 (2)PID: 12586 ###[Parent Process] Child process finished.
(1-5) (参考)fork()とforループを組み合わせて複数の子プロセスを起動する
forループを使えば、必要な分だけ子プロセスを生成する事も出来ます。下記の例では子プロセスを4個生成しています。また、各子プロセスのPIDと、その親プロセスのPID(PPID)も表示しています。この時、全ての子プロセスは同じ親プロセスに所属します。
(サンプル)
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0) {
//# 子プロセスの親プロセスPIDと、自身のPIDを出力
cout << "###[Child Process] (1)PPID: "<< getppid() <<" (2)PID: "<< getpid() << endl;
exit(0);
}
else {
//# 親プロセスのPIDを出力
cout << "###[Parent Process] (1)PID: "<< getpid() << endl;
cout << "###[Parent Process] Wait for Child Process to finish. " << endl;
wait(NULL);
cout << "###[Parent Process] Child process finished. " << endl;
}
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
(図161)①
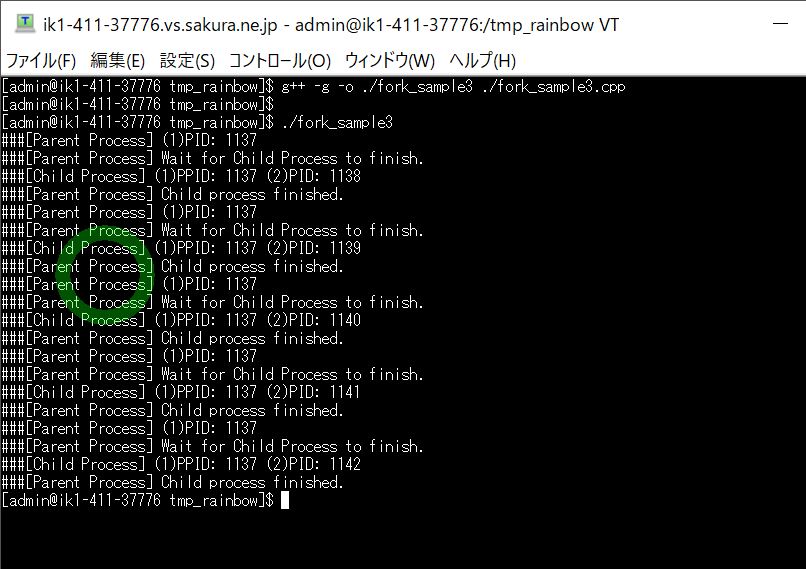
●実行結果
想定通り下記の4行1セット(親プロセスPID出力⇒子プロセス終了待ち⇒子プロセスPID出力⇒子プロセス終了判断)が、forkの回数分だけ発生しています。
###[Parent Process] (1)PID: 1137 ###[Parent Process] Wait for Child Process to finish. ###[Child Process] (1)PPID: 1137 (2)PID: [子プロセスのPID] ###[Parent Process] Child process finished. (結果例) [admin@ik1-411-37776 tmp_rainbow]$ ./fork_sample3 ###[Parent Process] (1)PID: 1137 ###[Parent Process] Wait for Child Process to finish. ###[Child Process] (1)PPID: 1137 (2)PID: 1138 ###[Parent Process] Child process finished. ###[Parent Process] (1)PID: 1137 ###[Parent Process] Wait for Child Process to finish. ###[Child Process] (1)PPID: 1137 (2)PID: 1139 ###[Parent Process] Child process finished. ###[Parent Process] (1)PID: 1137 ###[Parent Process] Wait for Child Process to finish. ###[Child Process] (1)PPID: 1137 (2)PID: 1140 ###[Parent Process] Child process finished. ###[Parent Process] (1)PID: 1137 ###[Parent Process] Wait for Child Process to finish. ###[Child Process] (1)PPID: 1137 (2)PID: 1141 ###[Parent Process] Child process finished. ###[Parent Process] (1)PID: 1137 ###[Parent Process] Wait for Child Process to finish. ###[Child Process] (1)PPID: 1137 (2)PID: 1142 ###[Parent Process] Child process finished.
<span style="font-size: 15px;">(図161)②</span>