<目次>
matmulとdotの違いについて(Pythonのnumpy・tensorflow)
(1-1) 両者の違い
(1-2) 両者の違い(実機確認)
matmulとdotの違いについて(Pythonのnumpy・tensorflow)
(1-1) 両者の違い
| 次元 (行列1\行列2) |
n=1 | n=2 | n>2 |
| n=1 (例:[1]) |
① 差異なし |
② 差異なし |
③ 差異なし |
| n=2 (例:[[1],[1]]) |
④ 差異なし |
⑤ 差異なし |
⑥ ▲差異あり ⇒詳細は「numpyの記事(★)」と「dotの記事(★)」を参照 |
| n>2 (例:[[[1],[1]],[[1],[1]]]) |
⑤ 差異なし |
⑧ ▲差異あり ⇒詳細は「numpyの記事(★)」と「dotの記事(★)」を参照 |
⑨ ▲差異あり ⇒詳細は「numpyの記事(★)」と「dotの記事(★)」を参照 |
| 次元 (行列1\行列2) |
n=1 | n=2 | n>2 |
| n=1 (例:[1]) |
① ▲差異あり ⇒tensorflowはエラー。numpyはベクトル内積計算。 |
② ▲差異あり ⇒tensorflowはエラー。numpyはベクトル内積計算。 |
③ ▲差異あり ⇒tensorflowはエラー。numpyはベクトル内積計算。 |
| n=2 (例:[[1],[1]]) |
④ ▲差異あり ⇒tensorflowはエラー。numpyはベクトル内積計算。 |
⑤ 差異なし |
⑥ 差異なし |
| n>2 (例:[[[1],[1]],[[1],[1]]]) |
⑦ ▲差異あり ⇒tensorflowはエラー。numpyはベクトル内積計算。 |
⑧ 差異なし |
⑨ 差異なし |
(1-2) 両者の違い(実機確認)
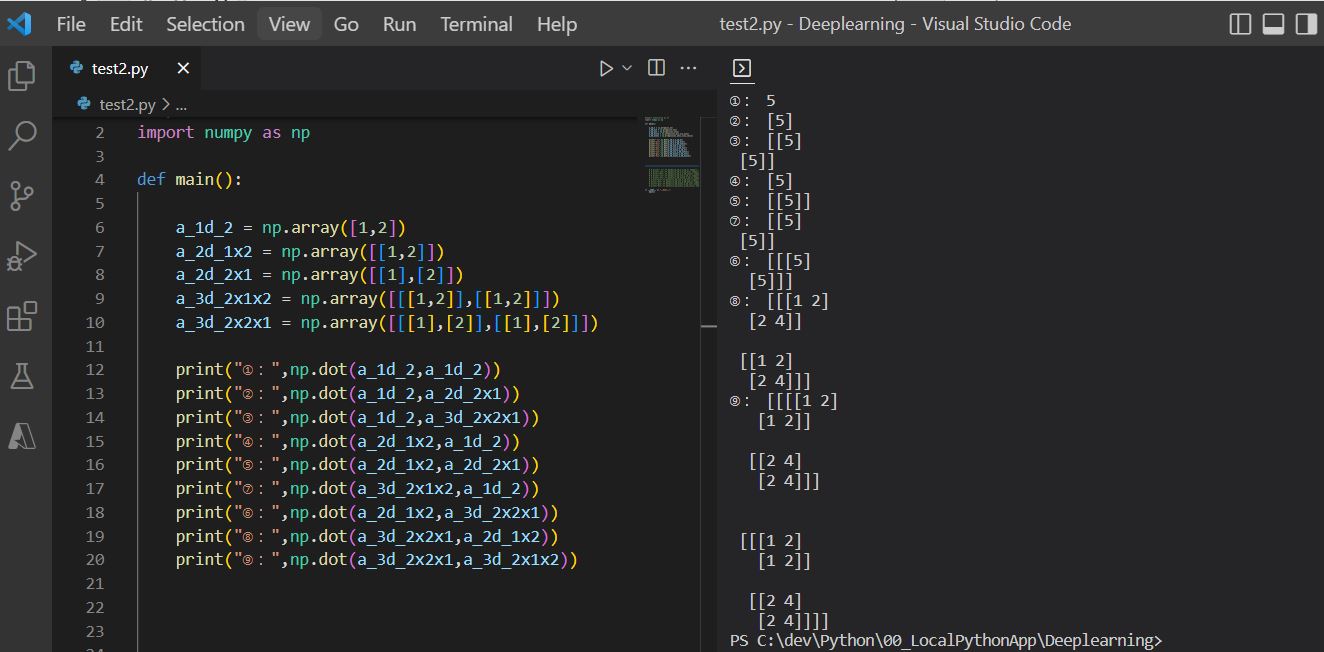
import numpy as np
def main():
a_1d_2 = np.array([1,2])
a_2d_1x2 = np.array([[1,2]])
a_2d_2x1 = np.array([[1],[2]])
a_3d_2x1x2 = np.array([[[1,2]],[[1,2]]])
a_3d_2x2x1 = np.array([[[1],[2]],[[1],[2]]])
print("①:",np.dot(a_1d_2,a_1d_2))
print("②:",np.dot(a_1d_2,a_2d_2x1))
print("③:",np.dot(a_1d_2,a_3d_2x2x1))
print("④:",np.dot(a_2d_1x2,a_1d_2))
print("⑤:",np.dot(a_2d_1x2,a_2d_2x1))
print("⑦:",np.dot(a_3d_2x1x2,a_1d_2))
print("⑥:",np.dot(a_2d_1x2,a_3d_2x2x1))
print("⑧:",np.dot(a_3d_2x2x1,a_2d_1x2))
print("⑨:",np.dot(a_3d_2x2x1,a_3d_2x1x2))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
(実行結果)
①: 5 ②: [5] ③: [[5] [5]] ④: [5] ⑤: [[5]] ⑦: [[5] [5]] ⑥: [[[5] [5]]] ⑧: [ [[1 2] [2 4]] [[1 2] [2 4]] ] ⑨: [ [ [[1 2] [1 2]] [[2 4] [2 4]] ] [ [[1 2] [1 2]] [[2 4] [2 4]] ] ]
(図121)
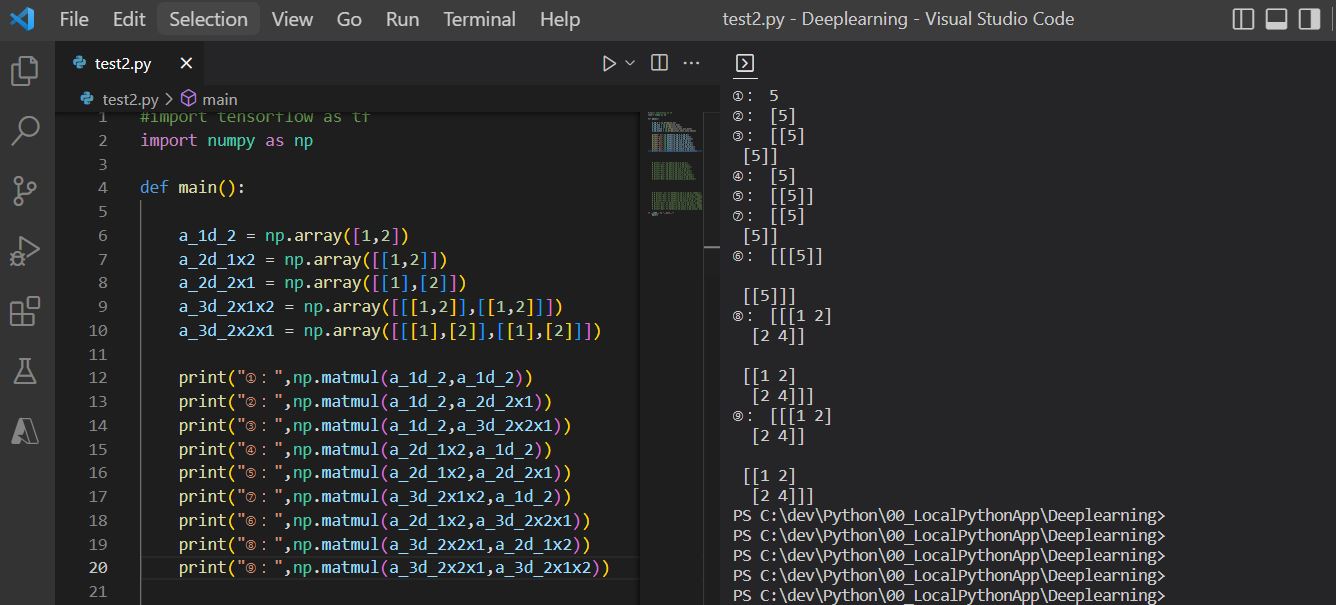
import numpy as np
def main():
a_1d_2 = np.array([1,2])
a_2d_1x2 = np.array([[1,2]])
a_2d_2x1 = np.array([[1],[2]])
a_3d_2x1x2 = np.array([[[1,2]],[[1,2]]])
a_3d_2x2x1 = np.array([[[1],[2]],[[1],[2]]])
print("①:",np.matmul(a_1d_2,a_1d_2))
print("②:",np.matmul(a_1d_2,a_2d_2x1))
print("③:",np.matmul(a_1d_2,a_3d_2x2x1))
print("④:",np.matmul(a_2d_1x2,a_1d_2))
print("⑤:",np.matmul(a_2d_1x2,a_2d_2x1))
print("⑦:",np.matmul(a_3d_2x1x2,a_1d_2))
print("⑥:",np.matmul(a_2d_1x2,a_3d_2x2x1))
print("⑧:",np.matmul(a_3d_2x2x1,a_2d_1x2))
print("⑨:",np.matmul(a_3d_2x2x1,a_3d_2x1x2))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
(実行結果)
①: 5 ②: [5] ③: [[5] [5]] ④: [5] ⑤: [[5]] ⑦: [[5] [5]] ⑥: [[[5]] [[5]]] ⑧: [ [[1 2] [2 4]] [[1 2] [2 4]] ] ⑨: [ [[1 2] [2 4]] [[1 2] [2 4]] ]
(図122)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def main():
a_1d_2 = np.array([1,2])
a_2d_1x2 = np.array([[1,2]])
a_2d_2x1 = np.array([[1],[2]])
a_3d_2x1x2 = np.array([[[1,2]],[[1,2]]])
a_3d_2x2x1 = np.array([[[1],[2]],[[1],[2]]])
# print("①:",tf.matmul(a_1d_2,a_1d_2).numpy())
# print("②:",tf.matmul(a_1d_2,a_2d_2x1).numpy())
# print("③:",tf.matmul(a_1d_2,a_3d_2x2x1).numpy())
# print("④:",tf.matmul(a_2d_1x2,a_1d_2).numpy())
# print("⑦:",tf.matmul(a_3d_2x1x2,a_1d_2).numpy())
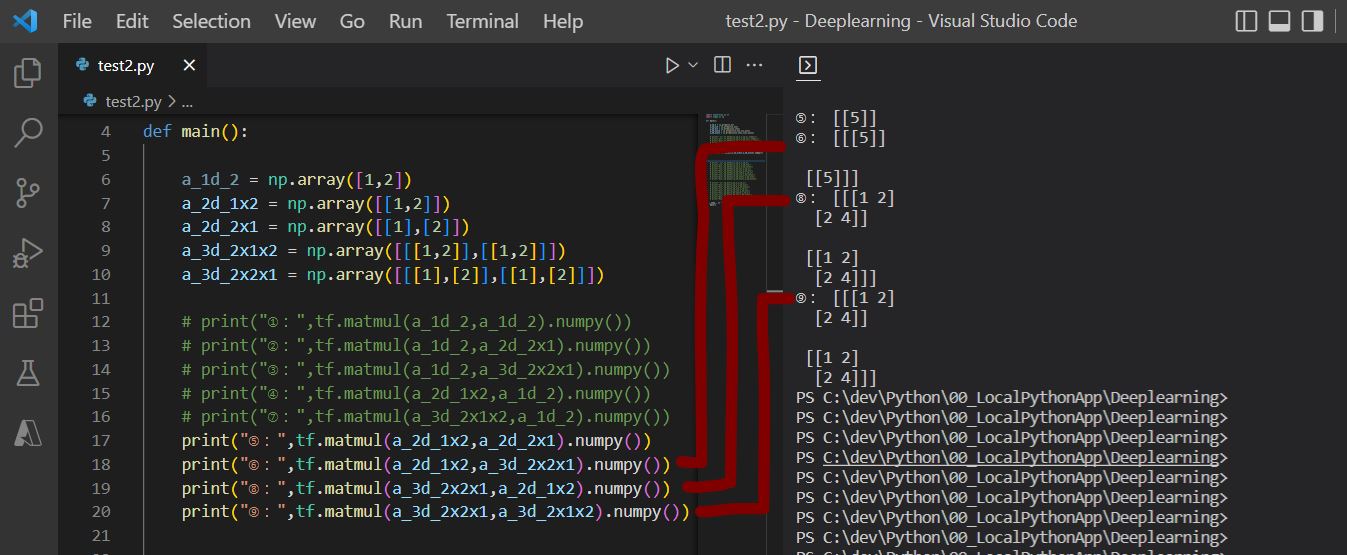
print("⑤:",tf.matmul(a_2d_1x2,a_2d_2x1).numpy())
print("⑥:",tf.matmul(a_2d_1x2,a_3d_2x2x1).numpy())
print("⑧:",tf.matmul(a_3d_2x2x1,a_2d_1x2).numpy())
print("⑨:",tf.matmul(a_3d_2x2x1,a_3d_2x1x2).numpy())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
(実行結果)
①:エラー(In[0] and In[1] ndims must be >= 2) ②:エラー(In[0] and In[1] has different ndims: [2] vs. [2,1]) ③:エラー(In[0] ndims must be >= 2) ④:エラー(In[0] and In[1] has different ndims: [1,2] vs. [2]) ⑦:エラー(In[1] ndims must be >= 2) ⑤: [[5]] ⑥: [[[5]] [[5]]] ⑧: [ [[1 2] [2 4]] [[1 2] [2 4]] ] ⑨: [ [[1 2] [2 4]] [[1 2] [2 4]] ]
(図123)