<目次>
(1) C++で変数にアスタリスク(*)が2つ付いている意味について
(1-1) 変数にアスタリスク(*)が2つ付いている意味
(1-2) 構文
(1-3) サンプルプログラム
(1-4) 補足:「int **ptr = new int*;」(左辺*2つ&右辺*1つ)について
(1) C++で変数にアスタリスク(*)が2つ付いている意味について
本記事では次のように変数の前にアスタリスクが(*)が2つ付いている意味についてご紹介します。
(例)
int **fruit_ptr;
(1-1) 変数にアスタリスク(*)が2つ付いている意味
//# ポインタ int *fruit_ptr1;
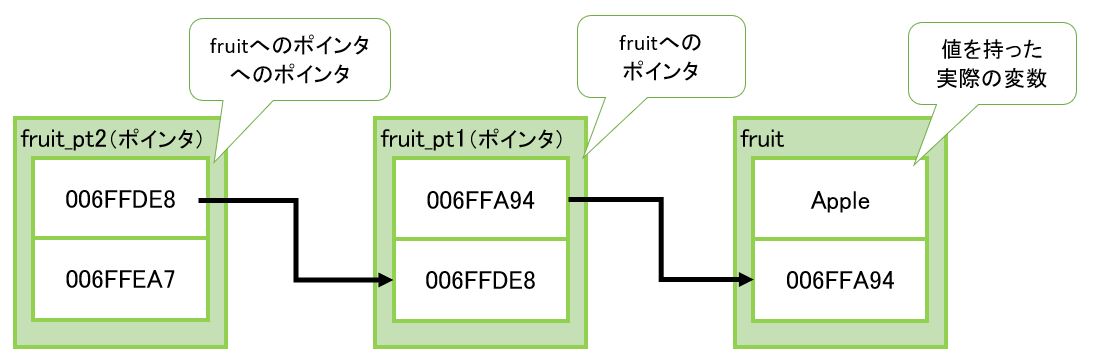
(1-2) 構文
//# 二重ポインタの定義(int型の例) int **変数名; //# 二重ポインタの値の書き換え **変数名 = 値;
(1-3) サンプルプログラム
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
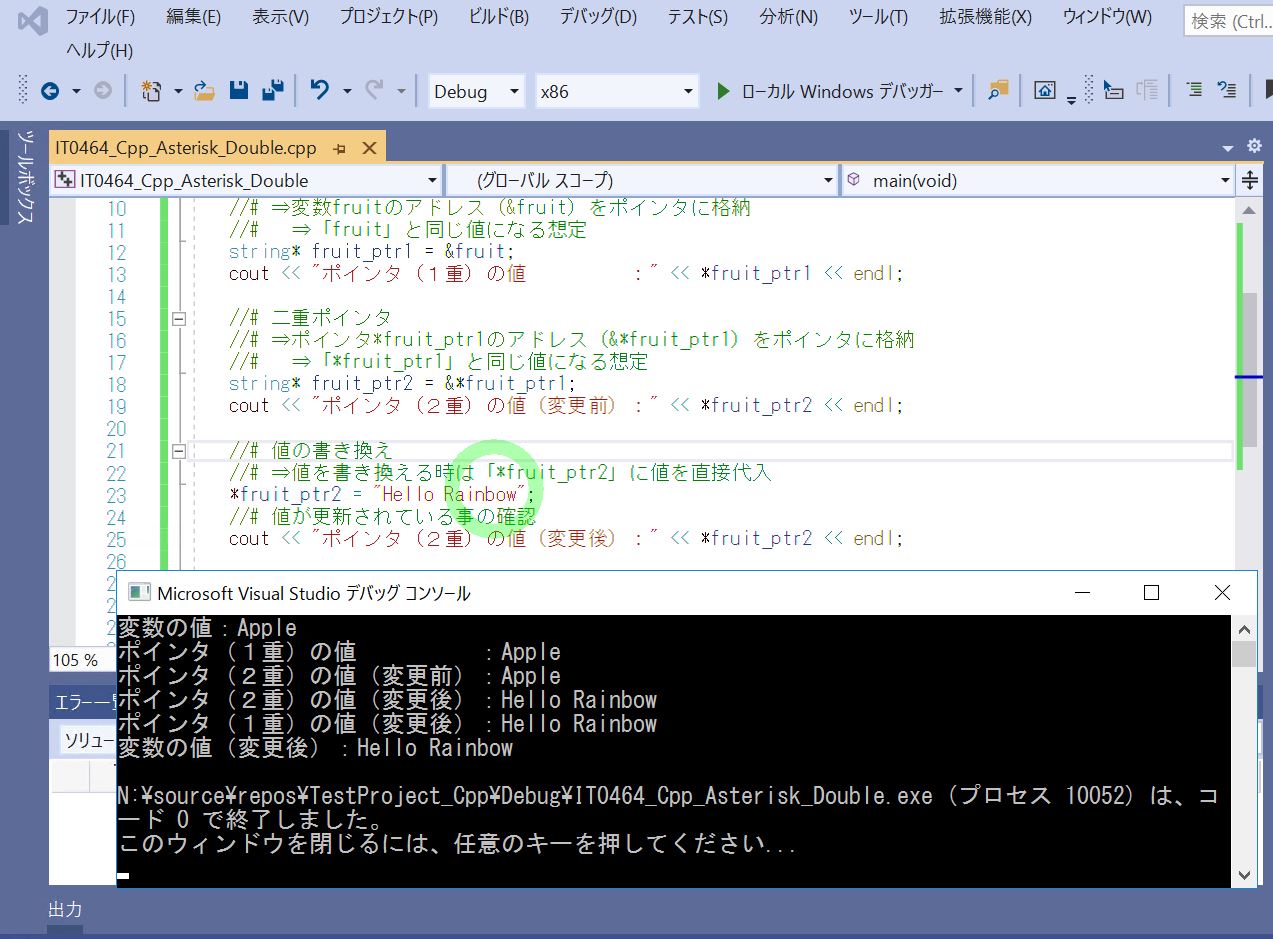
//# 変数
string fruit = "Apple";
cout << "変数の値:" << fruit << endl;
//# ポインタ
//# ⇒変数fruitのアドレス(&fruit)をポインタに格納
//# ⇒「fruit」と同じ値になる想定
string *fruit_ptr1 = &fruit;
cout << "ポインタ(1重)の値 :" << *fruit_ptr1 << endl;
//# 二重ポインタ
//# ⇒ポインタ*fruit_ptr1のアドレス(&*fruit_ptr1)をポインタに格納
//# ⇒「*fruit_ptr1」と同じ値になる想定
string *fruit_ptr2 = &*fruit_ptr1;
cout << "ポインタ(2重)の値(変更前):" << *fruit_ptr2 << endl;
//# 値の書き換え
//# ⇒値を書き換える時は「*fruit_ptr2」に値を直接代入
*fruit_ptr2 = "Hello Rainbow";
//# 値が更新されている事の確認
cout << "ポインタ(2重)の値(変更後):" << *fruit_ptr2 << endl;
//# 参照元の値が更新されているため「*fruit_ptr1」の値も変化
cout << "ポインタ(1重)の値(変更後):" << *fruit_ptr1 << endl;
//# 参照元の値が更新されているため「fruit」の値も変化
cout << "変数の値(変更後):" << fruit << endl;
}
(1-4) 補足:「int **ptr = new int*;」(左辺*2つ&右辺*1つ)について
⇒★cpp_ int**=new int*で掲載予定