<目次>
(1) 確率的勾配降下法(SGD)をロジスティック回帰に適用しPythonで実装した例をご紹介
(1-1) (課題)「勾配降下法」が抱える課題
(1-2) (対策)確率的勾配降下法(SGD)とは?
(1-3) (実装)Pythonで実装する際のポイント
(1-4) (実装例)サンプルプログラム
(1) 確率的勾配降下法(SGD)をロジスティック回帰に適用しPythonで実装した例をご紹介
(1-1) (課題)「勾配降下法」が抱える課題
\( b^{(k+1)} = b^{k}+\eta \sum^{N}_{n=1} (t_n-y_n) \)
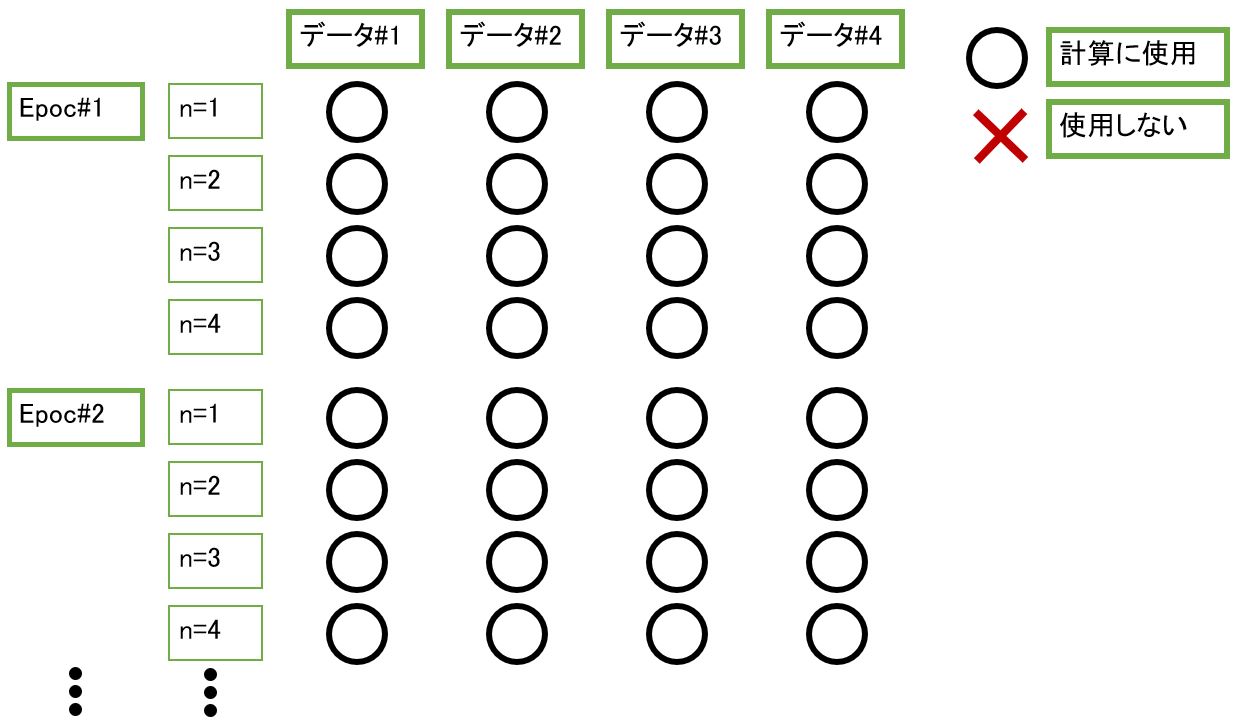
(1-2) (対策)確率的勾配降下法(SGD)とは?
\( b^{(k+1)} =b^{k} +\eta (t_n-y_n) \)
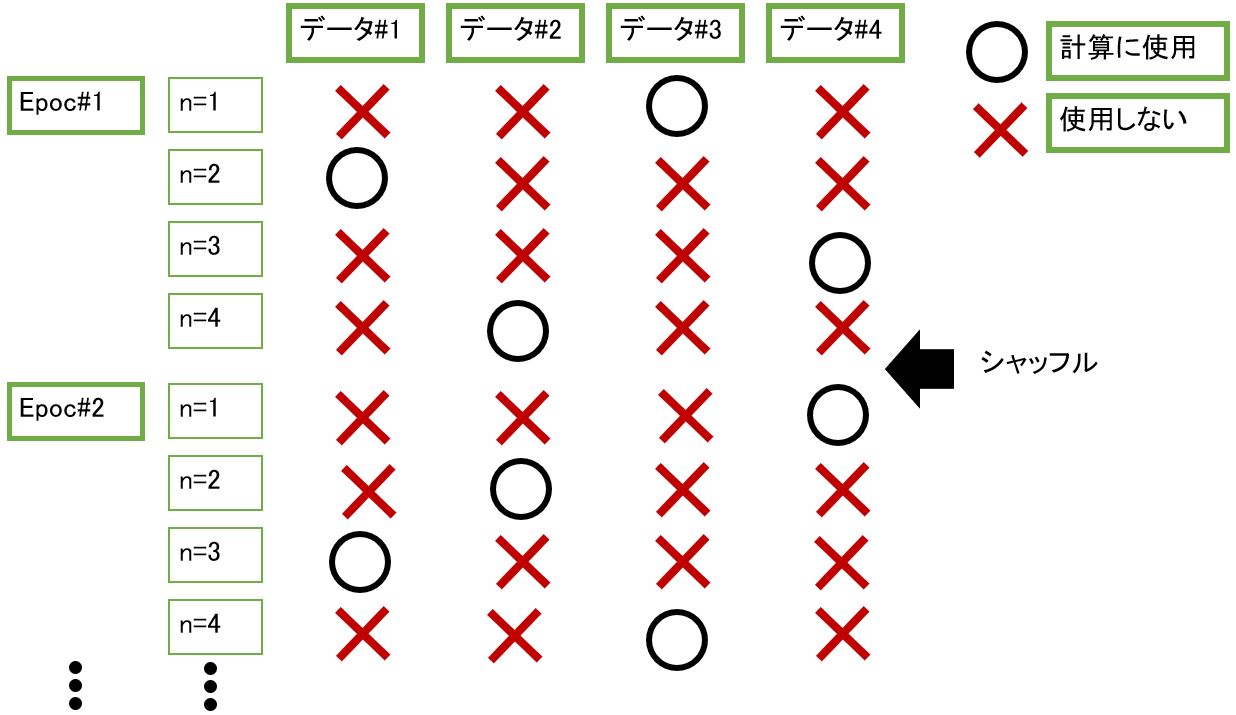
(1-3) (実装)Pythonで実装する際のポイント
############################################
# STEP5:学習
############################################
for epoc in range(25):
# バッチのデータ数だけ繰り返し
for n1 in range(N):
############################################
# STEP3:最適化手法の定義(例:勾配降下法)
############################################
# Σ(t[n]-y[n])の計算
# (tn-yn)、(tn-yn)xnの変数
t_y = 0
t_y_x = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([M],tf.float64), dtype = tf.float64, shape=[M])
for n2 in range(N):
# yの計算(モデルの出力)
y = tf.nn.sigmoid(np.dot(X[n2],weight)+bias)
# Σ(t[n]-y[n])の更新
t_y = t_y + (t[n2]-y[0])
# Σ(t[n]-y[n])xnの更新
t_y_x.assign_add(tf.math.scalar_mul((t[n2]-y[0]),X[n2]))
# 重みwの勾配(∂E(w,b)/∂w)の計算
dweight.assign(tf.math.scalar_mul((1.0/N),t_y_x))
# バイアスbの勾配(∂E(w,b)/∂b)の計算
dbias.assign([(1.0/N)*t_y])
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
############################################
# STEP5:学習
############################################
for epoc in range(25):
# バッチのデータ数だけ繰り返し
for n in range(N):
# データをシャッフル
X_,t_ = shuffle(X.numpy(),t.numpy())
xn = X_[n]
############################################
# STEP3:最適化手法の定義(例:勾配降下法)
############################################
# yの計算(モデルの出力)
y = tf.nn.sigmoid(np.dot(xn,weight)+bias)
# 重みwの勾配(∂E(w,b)/∂w)の計算
dweight = tf.math.scalar_mul((t_[n]-y[0]),xn)
# バイアスbの勾配(∂E(w,b)/∂b)の計算
dbias.assign([t_[n]-y[0]])
(1-4) (実装例)サンプルプログラム
############################################
# ロジスティクス回帰 - 確率的勾配降下法(Scotastic Gradient Descent)
############################################
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
# 入力xの次元
M = 2
# 入力データセットの数
N = 4
def or_gate(X_arg,t_arg):
############################################
# STEP1:モデルの定義
############################################
# 入力の電気信号xの初期化
X = tf.constant(X_arg, dtype = tf.float64, shape=[N,M])
# 重みwの定義 ⇒[1行×M列]
weight = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([M],tf.float64), dtype = tf.float64, shape=[M])
# バイアスbの定義 ⇒[1行]
bias = tf.Variable([0], dtype = tf.float64, shape=[1])
# シグモイド関数:y = σ(wx + b)の定義 ⇒[1行]
y = tf.Variable([0], dtype = tf.float64, shape=[1])
# 正解値tの定義([[0,1,1,1]) ⇒[n行×1列]
t = tf.Variable(t_arg, dtype = tf.float64, shape=[N])
# 重みwの勾配(∂E(w,b)/∂w)の定義
dweight = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([M],tf.float64), dtype = tf.float64, shape=[M])
# バイアスbの勾配(∂E(w,b)/∂b)の定義
dbias = tf.Variable([0], dtype = tf.float64, shape=[1])
# 学習率ηの定義
eta = 0.1
# Epocの定義
epoc = 0
############################################
# STEP4:セッションの初期化
############################################
# ⇒今回は不要
# (TensorFlow v2以降はSessionを使用しないため)
############################################
# STEP5:学習
############################################
for epoc in range(25):
# バッチのデータ数だけ繰り返し
for n in range(N):
# データをシャッフル
X_,t_ = shuffle(X.numpy(),t.numpy())
xn = X_[n]
############################################
# STEP2:誤差関数の定義
############################################
# ⇒今回は不要
# (確率的勾配降下法の式を使うため、途中経過の誤差関数Eは計算不要)
############################################
# STEP3:最適化手法の定義(例:勾配降下法)
############################################
# yの計算(モデルの出力)
y = tf.nn.sigmoid(np.dot(xn,weight)+bias)
# 重みwの勾配(∂E(w,b)/∂w)の計算
dweight = tf.math.scalar_mul((t_[n]-y[0]),xn)
# バイアスbの勾配(∂E(w,b)/∂b)の計算
dbias.assign([t_[n]-y[0]])
# 重みwの再計算
weight.assign_add(dweight)
# バイアスbの再計算
bias.assign_add(dbias)
# コンソール出力
decimals = 4
print("Epoc= ",epoc,
"No. = ", n,
"x1,x2 =", X[n].numpy(),
"t =", '{:01}'.format(tf.convert_to_tensor(t_[n]).numpy()),
"w1,w2 =", np.round(weight.numpy(),decimals),
"theta =", np.round(bias.numpy(),decimals),
"y =", '{:06.4f}'.format(tf.convert_to_tensor(y[0]).numpy()),
"dw1,dw2 =",np.round(dweight.numpy(),decimals),
"db =", np.round(dbias.numpy(),decimals))
def main():
# 初期値を設定し学習実行
X = [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
t = [0,1,1,1]
or_gate(X,t)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()